1.- What is the FNP?
The FNP is a combination of techniques, that helps (to the people that practise it) to improve the flexibility.
Phases:
- First you have to do a passive streching (20 seconds).
- After this, you have to do the isometric contraction (20 seconds).
- Third, you jave to take a break (3 or 5 seconds).
- And then, you have to do the maximumin the passive streching (20 seconds).
Examples:
- The cuadriceps:you have to be up against the wall and then, someone have to take your foot and try to put it in your back (with the hip always be up against the wall).
- Hamstrings: you have to sit down in front a wall with the feet touching it (the wall) and then, someone have to be behind you pushing your back while you put your arms ahead trying to touch the wall.


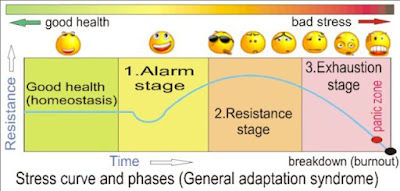
2.- The General Syndrome.
Is the process (of three phases) your body, when you are stressed that consist by assault-reaction.
-First phase: Alarm reaction stage.
Are the inicial symptoms the body experiences when you are under stress. The body start to answer with "fight or escape". These reactions is for make ready in front od dangerous situations. The heart rate and the adrenalin grow and the suprarenal gland start to releases cortisol.
-Second phase: Resistance stage.
If you don't solve the stress, your body will continue to secret the stress hormone and your blood pressure remains elevated and this effects will cause you exhaustion stage. This phase includes:
- Irritability: it's usually refer to anger or frustration.
- Frustration: arises from the perceived to the fulfillment of an individual's will or goal and it's increase when a will or goal is denided or blocked.
- Internal frustration: arise from challenges in fuilling personal goals.
- External frustration: it involve conditions outside an individual's control
- And poor concentration.
-Third phase: Exhaustion stage.
If you have cronic stress, it will drain your physical, emotional and mental resources with effects like:
- Fatigue: is a symptom that provocate (physical or mental) tired and exhaustion.
- Burnout: exhaustion of physical or emotional strength or motivation, usually as a result of prolonged stress or frustration.
- Depression: is a mental disorder that provocate feelings of sadnessand a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed.
- Anxiety: is a mental ilness too and this blocks you to continue with oyur normal life.
- Decreased stress tolerance.
- And weaking your inmune system.
3.- The Threshold law by Arnold Schultz.
This law explain the bodys adaptation as the result of physical efforts propose as a consecutive and appropiate way (in order to start to assimilate correctly). There are four cases:
- The first case is so far of the threshold, because there isn't training so therearen't improvements.
- In the second case, you can do the training if you do the works some times, but you will have more fatigue and efficiency reduction.
- The third case it's the best, here you get technique, muscular improvements...
-And the last case is where you won't have any tipe of improve, infact this case is where you have fatigue and an over training.
4.- The training Load.
training load is textual feedback on the strenuousness of a single training session. Training load calculation is based on the based on the consumption of critical energy resources (carbohidrates and proteins) during exercise.
- External load: refers to all player's locomotor movements and can be measured using electronictracking systems.
- Internal load: refers to be always positive and to be not stressed.
5.- The principles of training by Oliver (1985) and Zintl (1991).
-Oliver:
- Refers to the start to the stimulus of the physical conditioning.
- Refers to the start with the systems that go to the specific stimulus.
- Refers to the start of the answer of that specific stimulus.
-Zintl:
- The starts that start the adaptation.
- the starts that guarantee the adaptation.
- And the starts that apply a specific control of the adaptation.